Understanding Dental Resorption: What You Need to Know
Resorption is a natural but sometimes problematic process where the body's own cells break down and absorb the hard tissues of the tooth. While it’s often linked to trauma, infection, or orthodontic treatments, resorption can also occur spontaneously.
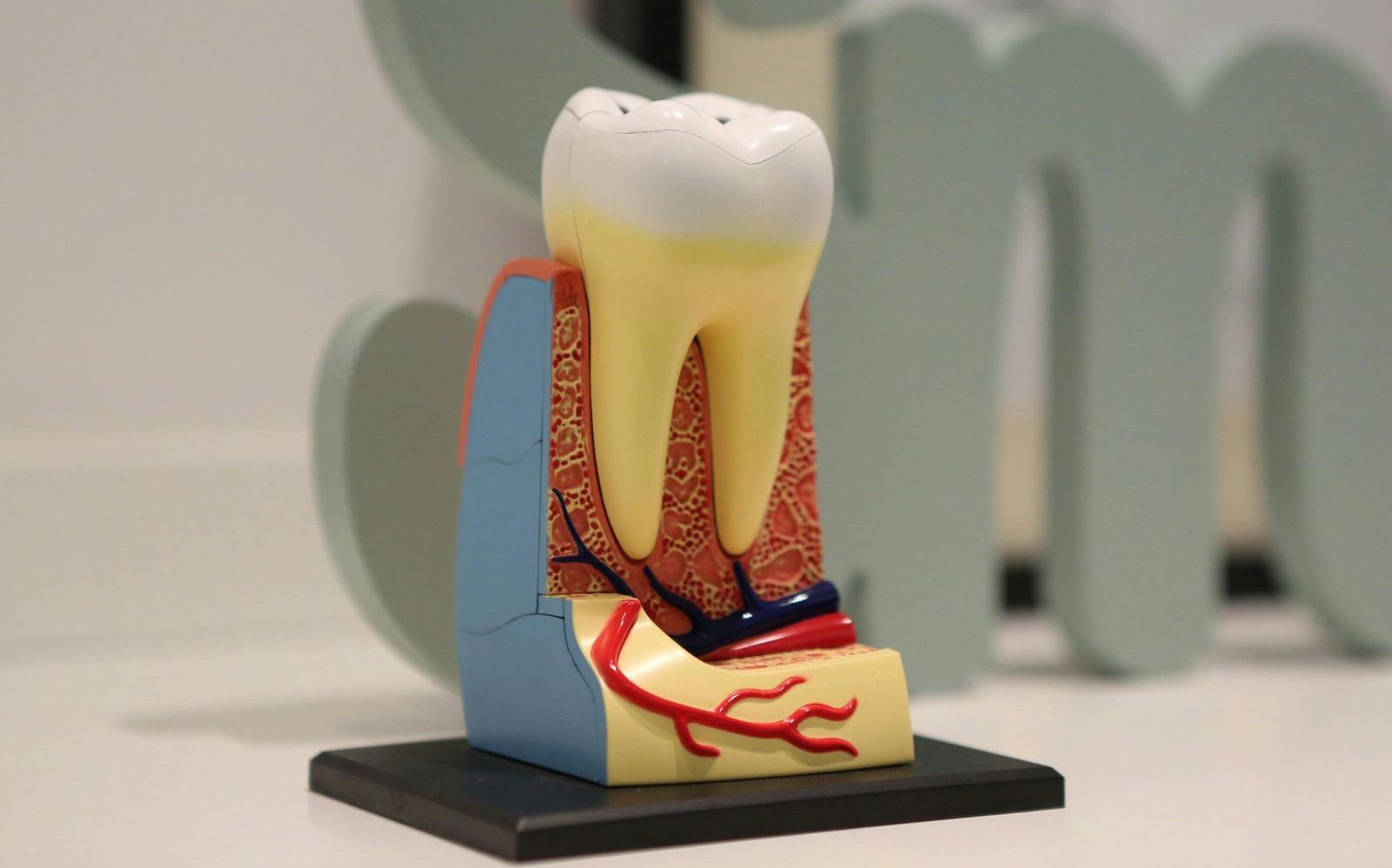
There are two primary types of resorption: external and internal. Both can lead to significant dental issues if not detected and managed early. The rate of resorption can vary widely, but can progress rapidly, making routine dental visits and radiographs all that more important. In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between these two types and what they mean for dental health.
What Is Resorption?
Resorption refers to the progressive destruction of the tooth’s root structure, which can compromise the tooth’s integrity and function. The process involves the abnormal activation of specialized cells called osteoclasts, which are responsible for resorbing (or breaking down) bone and tooth structure. In normal circumstances, resorption helps in the natural shedding of deciduous (baby) teeth to make way for permanent teeth. However, when it occurs in permanent teeth, it can lead to serious dental problems, such as weakening or early tooth loss.
External Resorption
External resorption occurs when the resorptive process originates from the outside of the tooth. This type of resorption is often linked to external factors, such as:
- Trauma or injury: A blow to the tooth can cause damage to the periodontal ligament and the surrounding bone, leading to resorption of the root from the outside. Think sport trauma, car accident, or fall.
- Orthodontic treatment: Although rare, prolonged or aggressive orthodontic treatment can cause pressure on the tooth, leading to external resorption.
- Infection or inflammation: When a tooth becomes infected or inflamed, the body’s immune response can result in the activation of resorptive cells, which start breaking down the root.
- Cyst or tumor: The presence of a cyst, tumor, or abnormal growth near a tooth can also lead to external resorption.
Externally resorbed teeth are often asymptomatic, but may show visible signs, such as a shortened root, irregular root or hallowed-out root, often detected by radiographs. In some cases, the resorption process may be so advanced that the tooth may become loose or even fall out. Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause (e.g., infection, trauma), and in severe cases, the tooth may need to be extracted.
Internal Resorption
In contrast, internal resorption begins within the tooth itself. This type of resorption is less common but can be just as serious. Internal resorption occurs when the pulp tissue (the soft inner part of the tooth) becomes inflamed or infected, leading to resorption of the tooth’s dentin and sometimes even the cementum.
Several factors can trigger internal resorption, including:
- Trauma or injury: A blow to the tooth may not just affect the root externally; it can also cause internal damage to the pulp, leading to resorption.
- Infection or abscess: Bacterial infection that reaches the pulp tissue can initiate an inflammatory response, causing internal resorption to progress.
- Tooth decay: Advanced cavities can eventually reach the pulp, causing infection and, ultimately, internal resorption.
- Orthodontic forces: Though less common, excessive or improper pressure from orthodontic braces may cause internal resorption.
Internal resorption is often painless in its early stages, but it can result in the tooth becoming structurally compromised and prone to breaking. Patients can sometimes see a pinkish hue due to the vascularization of resorptive tissue from the pulp. Dentists can often detect resorption through routine X-rays. In some cases, the resorption may progress rapidly, leading to the need for root canal treatment or even tooth extraction if the damage is severe.
Conclusion
Both external and internal resorption can lead to serious dental complications if not addressed promptly. While external resorption is often caused by trauma, infections, or external forces like orthodontic treatment, internal resorption tends to be a consequence of internal injury or infection to the pulp. Early detection through regular dental check-ups and X-rays is key to managing both types of resorption. One fundamental aspect providers look for to identify resorption is through changes in the tooth’s structure overtime to distinguish resorption from unique tooth structure or a carious lesion.
If you notice any signs such as tooth discoloration, discomfort, or loose teeth, it’s important to consult with your dentist for evaluation and appropriate treatment.
By understanding the causes and treatment options for both types of root resorption, patients can be better prepared to preserve their teeth and maintain good oral health for years to come.
Copyright © Dr. Annie Mazure-Schmidt
Subscribe To Our Blog